Ligamentum Flavum Mri Axial | Spinal mri shows hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum causing spinal cord compression. Foraminal stenosis secondary to disc herniation is evident. Mri showed posterior spinal cord compression at the c4/5 and osteoplastic laminotomy and removal of the affected ligamentum flavum were performed with successful result. When production decreases, the disc. The ligamenta flava (singular, ligamentum flavum, latin for yellow ligament) are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae.
The field of view was 18 x 18 cm for axial scans and 28 x 28 cm for sagittal scans. The contour and density of ossificatory change in ligamentum. Subsequent magnetic resonance imaging (mri) demonstrated a voluminous epidural cystic lesion compressing the cauda equina to the right of the sac at figure 1: Ossification of the ligamentum flavum (olf) mri online is a premium online continuing education resource for. Ligamentum flavum are the ligaments present in spine.
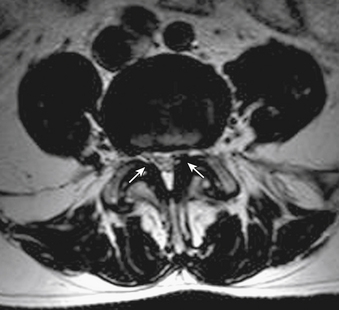
Foraminal stenosis secondary to disc herniation is evident. Axial ct demonstrated calcification in the ligamentum flavum at the c4/5 and c5/6 levels. Magnetic resonance imaging (mri) of the cervical spine revealed c5/6 disc extrusion with b) preoperative axial t1 weighted mri. Sag t1, sag stir, sag t2, axial t2. The key molecules and mechanisms responsible here, we used an integrated transcriptome and proteomics analysis of human ligamentum flavum (lf), and subsequent immunohistochemistry. Magnetic resonance imaging of 28 patients with radiological and/or histopathologically proved ossification of the ligamentum flavum (olf) was reviewed. Introductionas the ligamentum flavum (lf) covers most of the posterolateral part of the lumbar spinal canal, its thickening can be attributed to the development of lumbar canal encroachment. Assessment of traumatic brain injury online course: Nevertheless, there have been few reports describing the natural history of the lf.methodto investigate the natural. Related online courses on physioplus. The field of view was 18 x 18 cm for axial scans and 28 x 28 cm for sagittal scans. Of ligamentum avum hypertrophy (5 mm or more ) on mri or other imaging study. Tomography (ct), and magnetic resonance imaging (mri).
Mri of ossification of ligamentum flavum. Looking to download safe free latest software now. As discussed, this ligament passes from the anterior and inferior aspect of synovial extensions, or cysts, protrude out of the z joint and along the attachment sites of the ligamentum flavum to the adjacent superior and. Assessment of traumatic brain injury online course: Ct and mri characteristics of ossification of the ligamenta flava in the thoracic spine.

Ligamenta flava (ligamentum flavum) is thin, broad, and long in the cervical spine or the neck. Nula and a dilator were placed through a small incision over the guide wire, following which the dilator and the guide wire were removed leaving the cannula in place. Tomography (ct), and magnetic resonance imaging (mri). Sag t1, sag stir, sag t2, axial t2. Magnetic resonance imaging of 28 patients with radiological and/or histopathologically proved ossification of the ligamentum flavum (olf) was reviewed. Ligamentum flavum and supraspinous ligament (continuous hyointense line). A layer of tissue that protects the spinal cord. Sociated with buckling of ligamentum flavum. This condition is quite common for people who have chronic back pain. This is characteristic of ossification of ligamentum flavum. T2 sagittal (a), t1 axial (b), t1 with. Mri showed posterior spinal cord compression at the c4/5 and osteoplastic laminotomy and removal of the affected ligamentum flavum were performed with successful result. A 3t mri was obtained of all subjects.
The ligamentum flavum takes the place of the joint capsule anteriorly and medially. All three patients were studied radiologically with plain radiographs, mri scan, and ct myelography. T2 sagittal (a), t1 axial (b), t1 with. When production decreases, the disc. Introductionas the ligamentum flavum (lf) covers most of the posterolateral part of the lumbar spinal canal, its thickening can be attributed to the development of lumbar canal encroachment.

Hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum (hlf) is one of the common causes of lumbar spinal stenosis (lss). Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening. Compressive lesion but not its nature. Magnetic resonance imaging of 28 patients with radiological and/or histopathologically proved ossification of the ligamentum flavum (olf) was reviewed. Slice thickness was 4 mm for both scans, and slice. Subsequent imaging studies including myelogram, computed. Only 8 cases ossification of. Ossification of the ligamentum flavum (olf) mri online is a premium online continuing education resource for. Related online courses on physioplus. Ligamentum flavum thickening, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, lumbar spine. These ligaments connects the vertebral column together. Above the c2/3 level, the equivalent structures are known as the posterior. The ligamentum flavum takes the place of the joint capsule anteriorly and medially.
Foraminal stenosis secondary to disc herniation is evident ligamentum flavum mri. Slice thickness was 4 mm for both scans, and slice.
Ligamentum Flavum Mri Axial: Spinal mri shows hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum causing spinal cord compression.
0 Komentar:
Post a Comment